Multi-tenant architecture
Multi-tenant architecture is a design where a single instance of a software application serves multiple customers, or "tenants," who share the same underlying resources like a database and server but have their data and configurations securely isolated. This model is common in cloud services like SaaS, as it is more cost-efficient and easier to maintain for the provider since updates are made to a single application instance for all users.
Key characteristics
- Shared Resources: Tenants share the same application instance, operating system, hardware, and database infrastructure.
- Data Isolation: Each tenant's data is logically separated and kept private, making it invisible to other tenants.
- Customization: Tenants can often customize aspects of their experience, such as the user interface, without changing the core application code.
- Cost Efficiency: By sharing resources, the cost per user is lower, and the provider only needs to maintain a single application instance.
- Simplified Maintenance: Updates, security patches, and maintenance are managed centrally by the provider, ensuring all tenants are on the same version.
Analogy: An apartment building This architecture is like an apartment building where many tenants live in separate, private apartments but share common infrastructure like the foundation, roof, and plumbing.
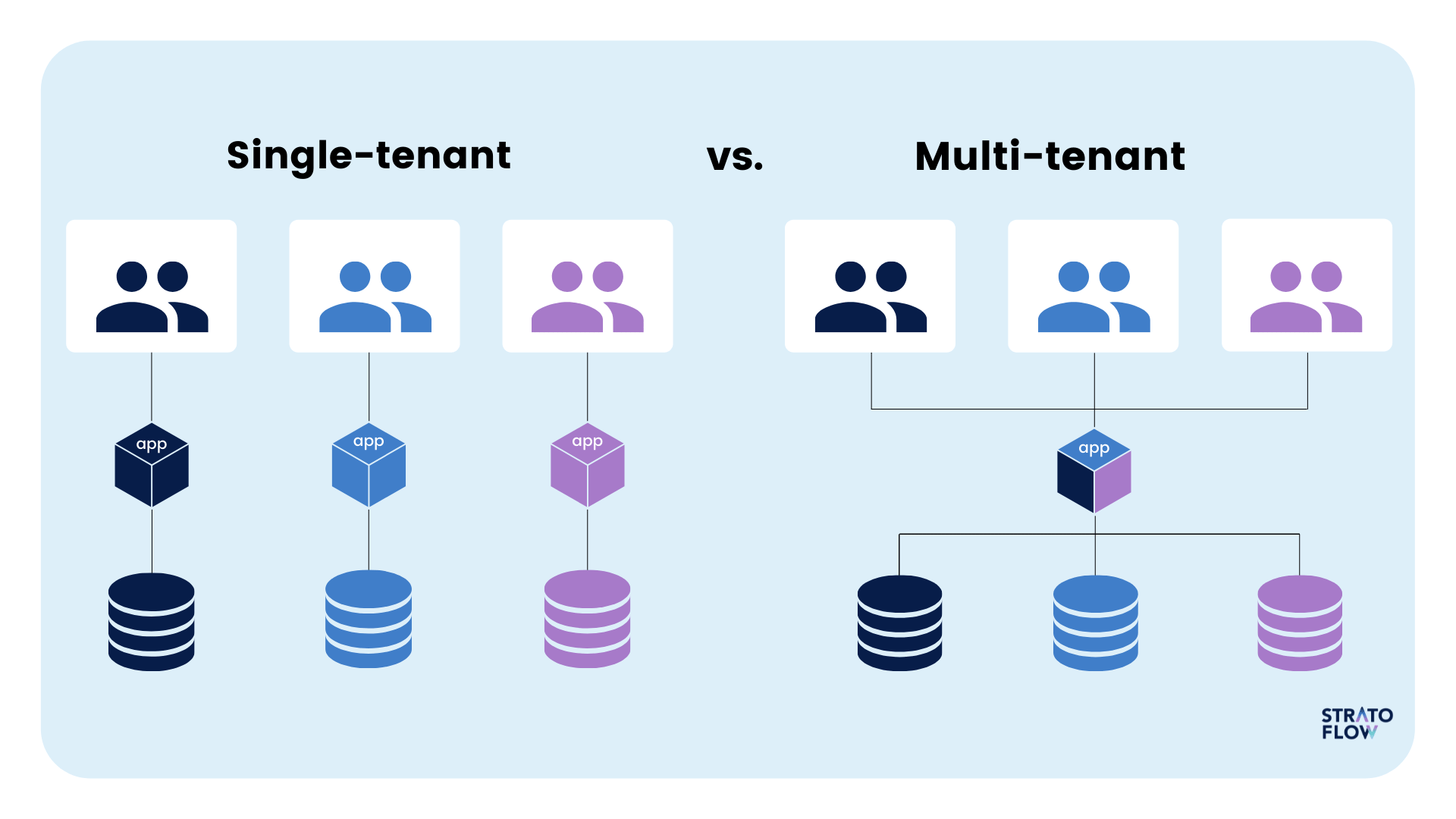
Comparison to single-tenant architecture
- Multi-tenant: A single, shared application instance serves many tenants, like multiple families in one building.
- Single-tenant: Each tenant has their own dedicated, isolated instance of the application, much like each family living in its own separate house.